The Renaissance style of Italy was slow spreading to Northern Europe. When Baroque was spreading in 16th Century Italy, France and England were developing their own Renaissandce styles. This classical style was then returned to by all of Europe making England and France the leaders as they had missed out on the Baroque period.
With the excavation of Pompeii in 1748, and the discovery of Greek and Etruscan sites, classical art found new energy. This began the classical revival of 1750 which then became the rigid dogmatic teaching of the Art Academies of Europe until the modern period.
Architecture
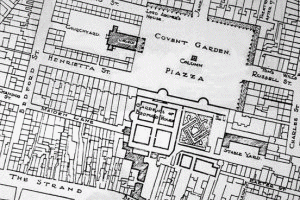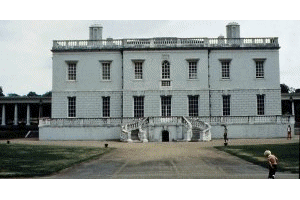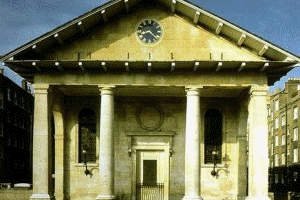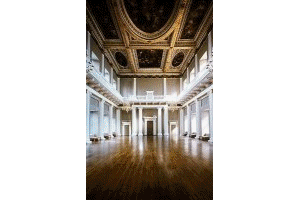 English
architecture remained Gothic until 1614 Inigo Jones (1573 to 1651)
travelled to Italy at the height of their Baroque period. Oddly Jones returned
to England with the Renaissance style of Palludio (Venice) and instituted
Classical design in place of Gothic.
English
architecture remained Gothic until 1614 Inigo Jones (1573 to 1651)
travelled to Italy at the height of their Baroque period. Oddly Jones returned
to England with the Renaissance style of Palludio (Venice) and instituted
Classical design in place of Gothic.
 Christopher
Wren (1632 to 1723) scientist, astronomer, engineer and architect, replanned
london after the Great Fire. He planned some 50 churches among them st. Pauls
Cathedral which is a combination of Classicism and Baroque.
Christopher
Wren (1632 to 1723) scientist, astronomer, engineer and architect, replanned
london after the Great Fire. He planned some 50 churches among them st. Pauls
Cathedral which is a combination of Classicism and Baroque.
In France, classicism followed the symetry and balance of the best Italian Renaissance style, Italian architects being employed to do the work.
1839 marks a Gothic revival when the houses of Parliment at westminster were built in "Tudor Gothic" style. At the same time the church of England proclaimed that Gothic was the only suitable style for a church.
Painting
The desire to return to the order of the Renaissance after the showy Baroque occured also in painting.


Poussin (1584 to 1665) -above left- and Claude Lorrain (1600 to 1682) - above right - studied the work of Raphael and Titian and then composed carefully balanced landscapes which frequently included ruins of Greek or Roman Temples.
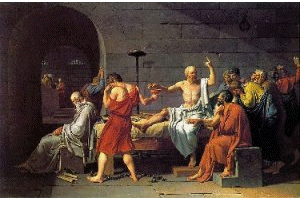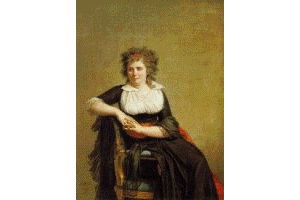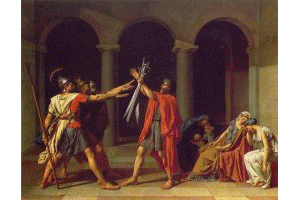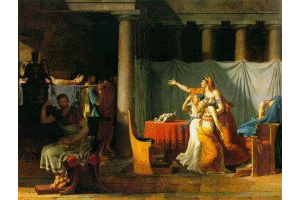 With
the French revolution (1789) came a severe military style of art based on
Roman example stories of heroism and fame. David (1744 to 1825) revolted
against the art of the French court. He was a supporter of the revolution
and threw off the decorative and superficial style of the French academies.
David expressed his beliefs of heroism and the "new order" through
a cold and severe style of painting.
With
the French revolution (1789) came a severe military style of art based on
Roman example stories of heroism and fame. David (1744 to 1825) revolted
against the art of the French court. He was a supporter of the revolution
and threw off the decorative and superficial style of the French academies.
David expressed his beliefs of heroism and the "new order" through
a cold and severe style of painting.

Ingres (1781 to1867) was a pupil of David who came under the influence of Raphael. His nude and portrait studies show little imagination but have a smooth highly finished appearance - a cold idea form of beauty.

Hogarth (1697 to 1764) was the founder of the English school of painting. He used wit and satire to expose the evils of society of his time.
 Joshua
Reynolds (1723 to 1792) gave the rich English upper class the portraits
and family groups they demanded. As england was a non-catholic country, religious
and subjects were not in demand.
Joshua
Reynolds (1723 to 1792) gave the rich English upper class the portraits
and family groups they demanded. As england was a non-catholic country, religious
and subjects were not in demand.
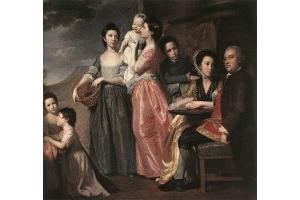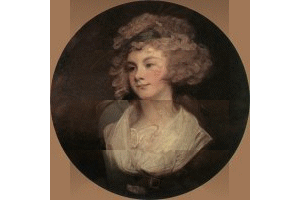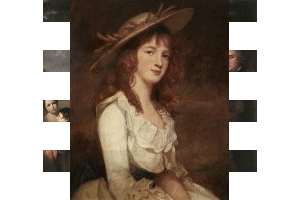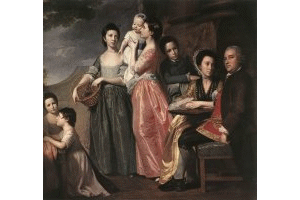
 Gainsborough
and Romney were 18th century portrait painters, Gainsborough also producing
landscapes which began the English landscape tradition of Constable
and Turner and in watercolour, Girtin, Cotman and Cox.
Gainsborough
and Romney were 18th century portrait painters, Gainsborough also producing
landscapes which began the English landscape tradition of Constable
and Turner and in watercolour, Girtin, Cotman and Cox.
In 1850 came a style which revolted against the artificiality of revivalist and Neo-Classical art. Called the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, these English painters claimed that since Raphael, art had become pagan and impure. They took subjects from life itself and created a dreamworld of ideal beauty and way of life. They made a return to the Middle ages with its ideas of hand craftmanship and shared produce - service in exchange for service instead of for money.Dante', Gabriel Rossetti, William Holman Hunt, John Everitt Millias, Ford Madox Brown were the prominent members of the Brotherhood. Their achievement lies not in what they were able to do, but in their revold against a tried academic style of art and an absence of quality and craftsmanship in the new industrial eye.